The Biomedical Engineering programme trains professionals who apply their knowledge of the human body and their engineering skills to biomedical issues. Professionals develop a suitable biomedical engineering product, or improve or validate a current product.
Biomedical engineers contribute to products that are used to examine sick or healthy bodies to enhance monitoring, prevention, diagnosis, treatment or aftercare. As a result, they become multifaceted professionals that are active in a broad range of companies and institutions. They can be employed with Philips or other medical product developing companies as part of the product development team. They can also make a contribution to new biomedical engineering solutions, e.g. in a research role, in an R&D laboratory. With institutions where biomedical products are used to benefit health among patients, such as care homes, a biomedical engineer can fill an advisory role.
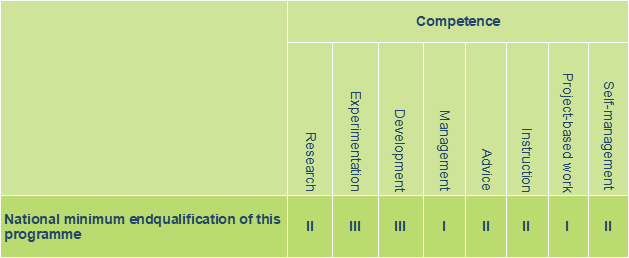
National Educational Programme
Body of Knowledge & Skills
Knowledge
Biology
- Biochemistry: cell regulation, biochemical reactions, bio-potentials, cellular processes, DNA replication, transcription, translation, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, energy supply, cell biology
- Physiology: metabolism, respiration, heat balance, excretion
- Anatomy: anatomical terminology, levels of organs in the human body, constitution and function of organ systems and skeleton, constitution and development of central nervous system, bio-mechanics
- Pathology: mechanisms of cell division and cell regulation, oncology, immunology, receptor-ligand kinetics, age-related diseases
Physics
- Electronics: electromagnetism, basic network theory (Ohm and Kirchhoff), signal analysis, linear time-invariant (LTI) systems
- Mechanics: laws of motion, biomechanics, motion analysis
- Optics: light, imaging, image analysis, microscopy
- Thermodynamics: conduction, radiation, thermal effects on the human body
- Materials science: strength theory, physical material properties
- Process dynamics and simple process description: measurement and control engineering
- Fluid theory: viscosity, density
- Radiation: atomic theory, ionising radiation, gamma radiation
Chemistry
- Basic chemistry: atomic constitution, reaction equations, chemical arithmetic, reactions in water, kinetics, chemical equilibrium
- Materials science: organic and polymer chemistry (synthesis, functional groups and reactions), chemical material properties
- Chemical basis of electronics
Mathematics
- Calculus: integration, differentiation, logarithms, complex numbers, powers, equations, Fourier and Laplace transformations
- Basic trigonometry: solve, reduce and differentiate functions, unit circle
- Statistics: data processing, normal distribution and confidence intervals, testing, descriptive statistics.
Ethics, laws and regulations, working in the medical domain
- Healthcare: organisation, trends and innovation and clinical practice
- Ethics: moral dilemmas in professional practice, privacy, data storage of personal data
- Safety, management, legislation: quality control (systems), management aspects, (patient) safety, performing risk analyses
- Patents, legislation and standards: CE certification, ISO standards, GMO legislation
Skills
- Research skills: Problem analysis, research questions, literature review, research planning and execution, systematic problem approach, quantitative and qualitative research skills
- Professional skills: Collaborating, having meetings, project-based work, planning, oral and written communication skills, providing, receiving and processing feedback, reflecting
- Product development skills: Going through the development cycle: iteration, reverse engineering, fast prototyping, assembly
- Programming and modelling: Creating flowcharts, Python programming, Excel modelling, data analysis, data mining, CAD drawing
- General laboratory skills: weighing, pipetting, mixing solutions (buffers and culture media) and specimens, keeping a lab journal, chemical arithmetic, microscopy, working with biological materials and bio-molecules
- Working with standard laboratory equipment: pH meter, centrifuge, voltage sources and meters, microscope, fume cupboard, electrophoresis equipment, safety cabinet, soldering station, 2D/3D production technology
- Working safely in the (technical) laboratory: working according to health and safety, VMT (veilige microbiologische technieken) and GLP (good laboratory practice) rules
The Body of Knowledge and Skills is a summary of graduates’ basic knowledge and basic skills which has been prepared by the HBO-programmes in consultation with the professional field. These are obtained during the first two years of education.
Institutions and professional fields
Institutions offering the programme keyboard_arrow_down
- Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences
Illustration of professional field keyboard_arrow_down
The professions, positions and roles of bachelors are mostly in the following professional domains. A few examples are included per domain.
Research en development
- Test engineer
- Research technician
- Data scientist
Analytical laboratory and production
- Medical engineer
- Analyst
- Quality controller
- Diagnostic laboratory technician
Engineering and process technology
- Product developer
- Development engineer
- Hardware engineer
- Software engineer
- Data engineer
Commerce, service and service provision
- QA/QC officer
- Application or product specialist
- E-health consultant
- Sales specialist medical devices
Typical course books keyboard_arrow_down
- Anatomie & Fysiologie voor Gezondheidszorg en Sport, L. Gregoir, A. van Straaten-Huygen
- Klinische Pathologie, C.B. van Heycop ten Ham
- Regels voor Robots, K. Gabriels
- Ethiek in ICT en Techniek, J. Rijnbout, M. Heerink e.a.
- Waardepropositie ontwerp, A. Osterwalder, Y. Pigneur
- Wiskunde voor het hoger onderwijs deel A, S. Kemme, W.Groen e.a.
- Biology, a global approach, N.A. Campbell, L.A. Urry e.a.
The list of typical textbooks serves as an illustration to give an impression of the level at which the subject is taught in the study programme.
