Applied Science trains students to fill a wide range of positions, ranging from the microbiological to the chemical and technological professional fields – from researchers to analysts. One of the characteristics of a broad first-year orientation in the fields of biology, chemistry, materials science and technology, as well as the variety of graduation opportunities with commercial companies, in the field of healthcare, at universities and research institutions.
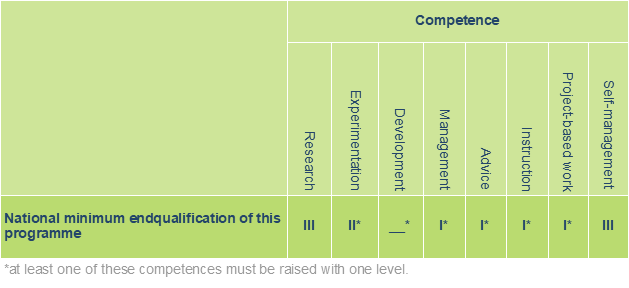
Following their first year, the students choose a direction that suits their interest and ambitions – directions that can be filled in with variables, causing a high level of flexibility among professional domains in which the graduates will kick off their careers. Because of the broad range of choice options, the programme puts a lot of focus on the self-management competence.
National Educational Programme
Body of Knowledge & Skills
Knowledge
- Basic chemistry: atomic and molecular construction, hybridisation, molecular structures, molecular bonds and interactions, reaction equations, chemical equilibria, reaction kinetics, redox reactions, buffer solutions, acids & bases, salts, catalysis
- Analytical chemistry: spectroscopy, chromatography
- Physical chemistry and physics: electrochemistry, light, mass balances
- Organic chemistry: synthesis of functional groups, reaction mechanisms, substitution and elimination reactions, alkanes, alkenes, carboxylic acids, esters, aromatics, alcohols, ethers, alkyl halides, isomers, enantiomers, stereochemistry
- Polymer chemistry and materials science: monomers, polymers, biopolymers, radical polymerisation, physical properties
- Statistics: data processing, normal distribution and confidence intervals, testing, calibration
- Mathematics: chemical arithmetic, functions, differential calculus
- Biochemistry: biomolecules, DNA, RNA, proteins, sugars, fats
- Cell biology: structure and function of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, metabolism, transport, cell membrane
- Microbiology: growth and classification of micro-organisms, pathogenicity mechanisms, infectious diseases
- Safety, health and environment: sustainability, chemical and biological safety
Skills
- General laboratory skills: weighing, pipetting, micro-pipetting, creating solutions (e.g. buffers), keeping a lab journal, chemical arithmetic, microscopy
- Chemical analysis methods: titrimetry, spectrometry (e.g. UV/VIS, IR, NMR), chromatography (e.g. GC-FID) and other methods such as electrochemistry
- Working with standard laboratory equipment: pH meter, spectrophotometer, refractometer, centrifuge, voltage sources, microscope, fume cupboard
- Laboratory techniques: distillation, extraction, reflux, microbiological techniques, synthesis techniques
- Working safely: both in the laboratory and in the workplace
- Information skills: word processing, spreadsheets and presentations
- Research skills: problem analysis, research questions, literature research, research planning and performance
- Social and communication skills: collaborating, having meetings, reporting (lab journal, research report), oral presentations, project-based work, self-management
The Body of Knowledge and Skills is a summary of graduates’ basic knowledge and basic skills which has been prepared by the HBO-programmes in consultation with the professional field. These are obtained during the first two years of education.
Institutions and professional fields
Institutions offering the programme keyboard_arrow_down
- Fontys University of Applied Sciences, Eindhoven
- Zuyd University of Applied Sciences, Heerlen
Illustration of professional field keyboard_arrow_down
The professions, positions and roles of bachelors are mostly in the following professional domains. A few examples are included per domain.
Research & Development
- Biological laboratory research assistant
- Chemical laboratory research assistant
- Vaccine development
- Research into materials
- Research into nutrients
Analytical laboratory and production
- Analytical chemist for product quality control
- Analyst with a hospital or diagnostics centre
Engineering and process technology
- Process engineer
Commerce, service and service provision
- Patent cases assistant
Typical course books keyboard_arrow_down
- Chemistry, J.E. McMurry. R.C. Fay e.a.
- Organic Chemistry, D. Klein
- Principles of Instrumental Analysis, D.A. Skoog, F.J. Holler e.a.
- Campbell Biology, L.A. Urry, M.L. Cain e.a.
- Molecular Biology of the Cell, B. Alberts, A. Johnson
- Brock Biology of Microorganisms, M.T. Madigan, K.S. Bender e.a.
- Klinische chemie en hematologie voor analisten, E. ten Boekel, B.A. de Boer
- Procestechnologie, delen 2, 3 en 4, VAPRO
- Kunststof- en polymeerchemie, R. van der Laan
- Statistiek om mee te werken, A. Buijs
The list of typical textbooks serves as an illustration to give an impression of the level at which the subject is taught in the study programme.
