The higher professional course in Chemistry leads to a job as experimental laboratory
worker. The professional field of chemistry is the key element. It can be roughly divided into
three major components: analytical chemistry, research into and synthesis of molecules and
compounds and the development of products based on functional molecules or components.
Chemists working in research laboratories in government institutions and large companies are responsible for the practical implementation of a complete or partial research project. They develop and build experimental test setups, conduct and interpret experiments (or arrange for this to be done), draw conclusions and make recommendations. In research laboratories in the SME sector, the approach adopted is often less fundamental and more applied. In this case, the chemists tasks also include directing, organising and coordinating the work.
In other domains, including application or manufacture, the chemist is mainly employed as an experimental laboratory worker. This can be in environmental laboratories or quality control and production laboratories in the organic, biochemical and analytical fields or similar laboratories. This usually involves conducting complex and intricate experiments that challenge graduates’ practical skills and analytical ability. In the manufacturing domain, chemists are involved in product development and introduction, particularly the aspects completed in the laboratory.
National Educational Programme
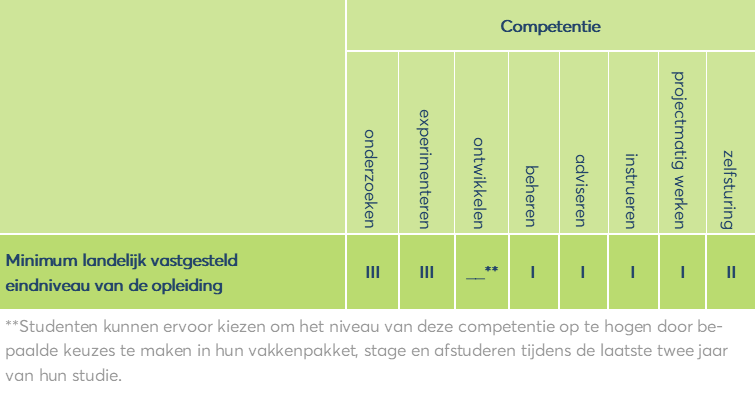
Body of Knowledge & Skills
Knowledge
- Analytical chemistry: spectroscopy, chromatography
- Basic chemistry: atomic and molecular structure, reactions in water, chemical balance
- Biochemistry: biomolecules, protein and enzyme chemistry
- Physical chemistry (e.g. electrochemistry, phase theory, colloid chemistry)
- Information technology (e.g. chemometrics, experimental design, simulation and design programs)
- Physical applications (e.g. optics, electronics)
- Organic chemistry: synthesising functional groups, reaction mechanisms
- Polymer chemistry and materials science
- Statistics: data processing, normal distribution, confidence intervals, testing
- Thermodynamics and kinetics
- Health, safety and environment
- Mathematics: chemical calculations, functions, differential and integral calculus
Skills
- General laboratory skills: weighing, pipetting, making solutions (buffers), keeping a lab journal, chemical calculations
- Chemical analysis methods: spectrometry (e.g. UV/VIS, IR, AAS, NMR, ICP), chromatography
(e.g. GC, GC-MS, HPLC) and other methods such as titrimetry, electrochemistry, enzyme analysis, bonding analysis - Computer skills: word processing, spreadsheets, chemical drawing programs, presentation techniques
- Research skills and systematic approach to problems: problem analysis, preparing research
questions, desk research, research planning and implementation - Social and communication skills: collaborating, meetings, written reporting (lab journal, research report), oral presentation, project-based work
- Safe working in the laboratory in accordance with HSE rules
- Using standard laboratory equipment: pH meter, spectrophotometer, centrifuge, power sources, electrophoretic equipment
- Using setups for organic synthesis: reflux, distillation, extraction, evaporators
The Body of Knowledge and Skills is a summary of graduates’ basic knowledge and basic skills which has been prepared by the HBO-programmes in consultation with the professional field. These are obtained during the first two years of education.
Institutions and professional fields
Institutions offering the programme keyboard_arrow_down
- Avans University of Applied Sciences, Breda
- Avans University of Applied Sciences, Den Bosch
- HAN University of Applied Sciences, Nijmegen
- Hanze University of Applied Sciences, Groningen
- HU University of Applied Sciences Utrecht
- HZ University of Applied Sciences, Vlissingen
- Inholland University of Applied Sciences, Amsterdam
- NHL Stenden University of Applied Sciences, Emmen
- NHL Stenden University of Applied Sciences | VHL University of Applied Sciences, Leeuwarden
- Rotterdam University of Applied Sciences
- Saxion University of Applied Sciences, Deventer
- Saxion University of Applied Sciences, Enschede
- University of Applied Sciences Leiden
- Zuyd University of Applied Sciences, Heerlen
Illustration of professional field keyboard_arrow_down
Occupations, jobs and roles for graduates are mostly to be found in the following professional
domains. A few examples are given for each domain.
Research and development
- Chemical laboratory research worker
- Product development based on functional components
- Analytical chemist
- Research into new functional molecules or compounds
Application and production
- Analytical chemist in a quality control laboratory
- Laboratory-scale production of molecules or preparations for diagnostic tests or research
purposes
Engineering and manufacturing
- Developing analyses for quality control
- Research into parameters of chemical reactions or processes for upscaling
Commerce and customer service
- Safety and environmental consultant
- Sales engineer
Typical course books keyboard_arrow_down
- Chemistry, J.E. McMurry. R.C. Fay e.a.
- Campbell Biology, L.A. Urry, M.L. Cain e.a.
- Elements of Physical Chemistry, P. Atkins, de Paula
- Organic Chemistry, P.Y. Bruice
- Quantitative Chemical Analysis, D. C. Harris
- From Polymers to Plastics, A.K. van der Vegt
- Principles of Instrumental Analysis, D.A. Skoog, F.J. Holler e.a.
- Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, J. Miller, J.C. Miller
- Exact communiceren, R. van der Laan
- Wiskunde voor hoger onderwijs, S. Kemme, W. Groen e.a.
The list of typical textbooks serves as an illustration to give an impression of the level at which the subject is taught in the study programme.
